1. Technical introduction
(1)HDO Structure
HDO is composed as follows.
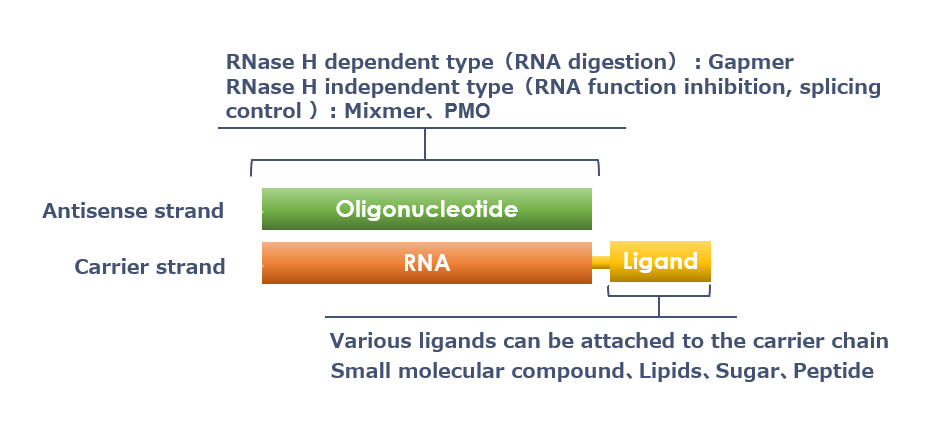
Antisense strand (DNA, Gapmer, PMO etc.) : Has a medicinal effect
Carrier strand(RNA) : Transport active strand (medicinal effect) to disease site
Ligand : By binding a substance that specifically binds to a specific receptor to the carrier strand, it transports the active strand to a targeted disease site
(2)HDO's mechanism of action
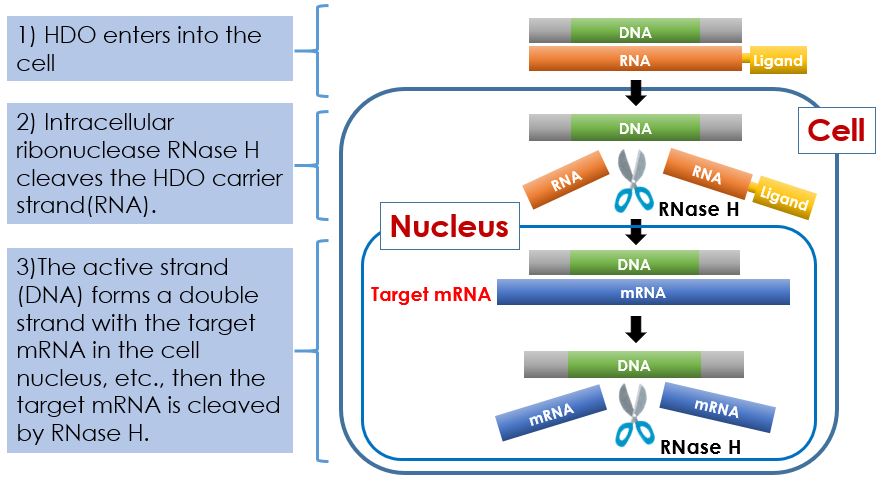
The mechanism of action of the RNaseH-dependent antisense effect is as follows:
Step1
The HDO carrier strand (RNA) incorporated into the cell is cleaved by RNase H (enzyme).
Step2
The antisense strand (DNA) remaining after cleavage binds to the target mRNA.
Step3
When the antisense strand (DNA) binds to mRNA, it becomes DNA / RNA structure again, and RNase H cleaves the target mRNA.
Step4
As mRNA is cleaved, mRNA expression is suppressed, and drug efficacy is demonstrated.
※RNase H has the property of cleaving RNA among double strands composed of DNA / RNA.
*HDO can also respond to RnaseH-independent antisense effects (eg exon skipping).
(3)Strengths of HDO technology
HDO has the following strengths:
- By linking the ligand to the carrier strand, it is possible to selectively deliver the antisense strand to the diseased site through the binding between this ligand and the receptor expressed on the cell surfaces, so that high efficacy can be obtained.
- In the case of HDO, since the ligand is attached to the carrier strand, inhibition of knockdown activity by the antisense strand, which is the active body, is unlikely to occur.
- HDO binds to different proteins than single-stranded ASO in the cell, and thus has higher nuclear translocation than ASO. Therefore, it is an advantageous technology for both knockdown and exon skipping.
- There is no need to make the linker used for binding the ligand to the carrier strand prone to breaking easily
- The position and the number of ligands bound to the carrier strand can be freely selected
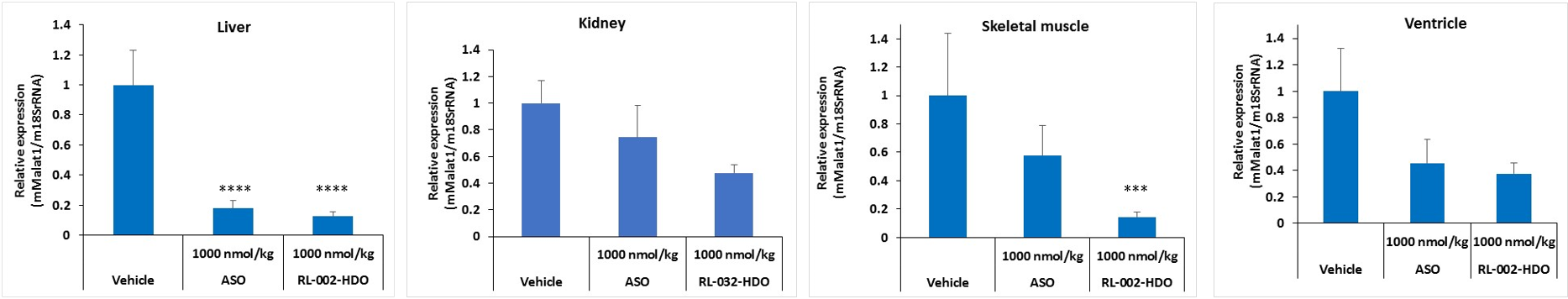
(4)Ligand library
We are developing a ligand library as a delivery technology for HDO using ligands. We are mainly focusing on the development of ligands targeting skeletal muscle, myocardium, immune cells, central nervous system, lungs and kidneys.
An example of ligand development is shown below.
(5)HDO technology overview material
Click here for an overview of HDO technology.
2. Business Introduction
(1)Business model
Rena has the following three business lines.
①Licensing
②Collaborative R&D
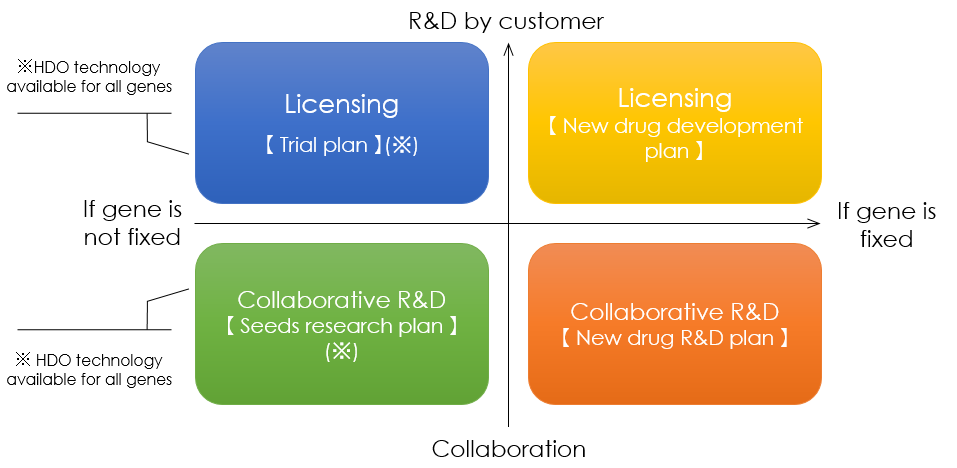
③HDO manufacturing
(2)Business lines
①Licensing
This is our business structure for licensing out HDO technology.
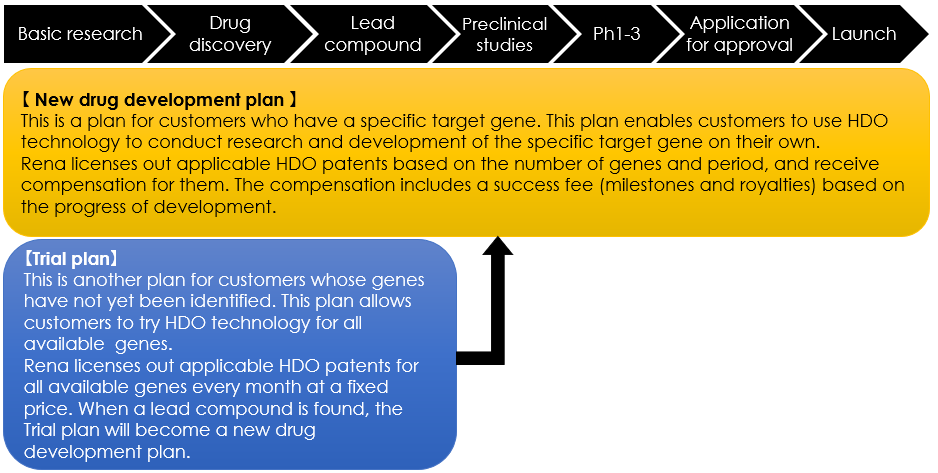
②Collaborative R&D
This is our business structure or collaborative R&D with customers, in which Rena designs and provides HDO compounds and moves collaborative R&D forward to find lead HDOs.
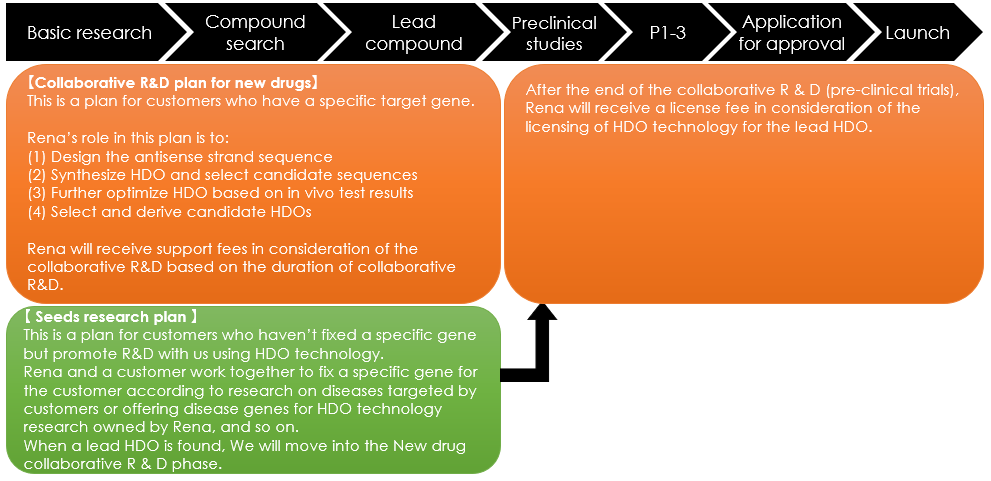
③HDO manufacturing
This is our business structure for the HDO manufacturing business in which Rena manufactures, supplies and sells HDOs for target genes only for research and development.
For inquiries about our technology
